Recently, Professor Mu Jianjun’s team at the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU) published original findings in MedComm (IF = 10.7) entitled “Impact of Blood Pressure Across the Life Course on Arterial Stiffness in Midlife: The Mediating Role of Metabolic Factors”.

Using data from the Hanzhong Adolescent Hypertension Study, the research team enrolled 1,448 participants aged 6-18 years who entered the study in childhood and were followed for over 30 years, and conducted an integrated analysis of how blood pressure (BP) in childhood and adulthood, as well as cumulative BP burden, affects brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV), an index of midlife arterial stiffness.
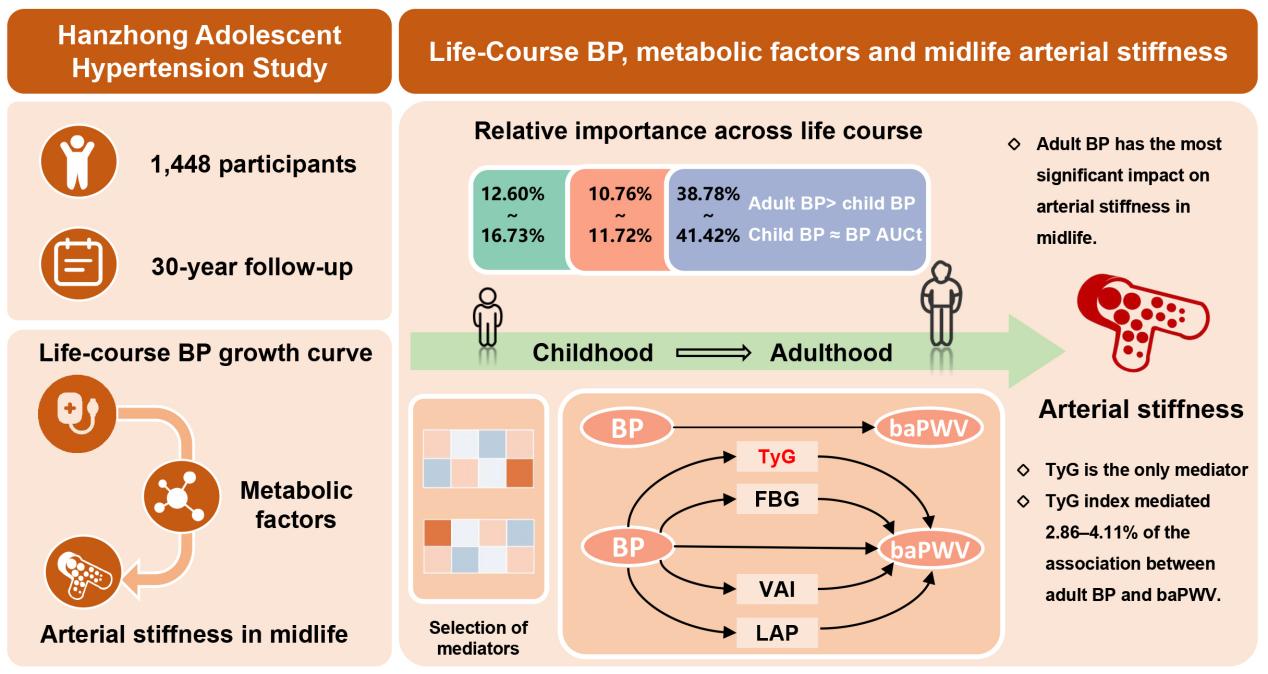
The study found that BP across the life course is significantly associated with arterial stiffness in midlife. Childhood BP, adulthood BP, and cumulative long-term BP burden were all significantly related to midlife arterial stiffness, with the strongest association observed for adulthood BP, whose contribution exceeded 40%; nevertheless, the roles of childhood BP and cumulative long-term BP burden should not be overlooked. The triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index emerged as an important mediator of the association between adulthood BP and arterial stiffness, indicating insulin resistance as a key mechanistic pathway. In the sex-stratified analyses of this study, the mediating effect of insulin resistance was observed primarily in men.
The research clarifies the critical value of BP management spanning early life → adulthood → midlife, and underscores the need to incorporate BP monitoring and metabolic health management into a life-course strategy. The findings not only enrich theoretical understanding of the occurrence and development of arterial stiffness, but also identify new targets for clinical intervention, such as insulin resistance-related metabolic markers, and provide fresh theoretical basis and practical insights for the prevention and control of cardiovascular disease.

The study was led by the FAH of XJTU. Associate Researcher Wang Yang is the first author, and Professor Mu Jianjun is the corresponding author.
Full text link: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/mco2.70440