On August 21, 2025, the team led by Professors Ma Xiancang and Zhu Feng from the Department of Psychiatry, the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU), published an original research article entitled “Distinct Gut Microbial Signatures and Diminished Anti-inflammatory Effect of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Schizophrenia With Immune Activation” in the prestigious psychiatric journal Schizophrenia Bulletin. This study firstly represents the systematic analysis of the multi-omics relationships among gut microbiota characteristics, serum immune activation biomarkers, and short-chain fatty acid (SCFA) levels in schizophrenia (SCZ) patients with immune activation. The findings further elucidate the role of gut microbiota metabolites, SCFAs in particular, in the immune dysregulation associated with SCZ.

The study enrolled 297 patients with SCZ and 301 healthy controls. Peripheral immune activation subtypes were defined based on four serum immune mediators, and metagenomic sequencing together with SCFA level measurements was performed on fecal and serum samples from 144 patients and 146 controls.
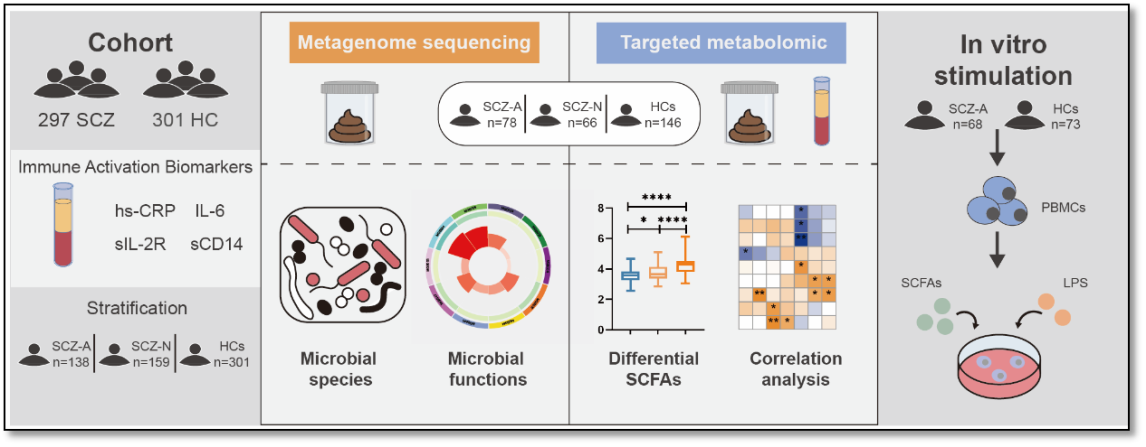
The study found that a subset of SCZ patients (approximately 46.5%) exhibited peripheral immune activation. This subgroup displayed unique gut bacterial signatures, specifically enriched species capable of producing SCFAs and an enhanced microbial capacity for SCFA biosynthesis. Targeted metabolomics further confirmed that serum and gut levels of acetate, propionate, butyrate, and total SCFAs in this subgroup were significantly higher than those in non-immune-activated patients and healthy controls. Moreover, the study found that the anti-inflammatory effects of SCFAs were markedly diminished in immune-activated patients, while their ability to induce pro-inflammatory cytokine secretion was enhanced. These findings suggest that impaired immunoregulatory functions of SCFAs may contribute to the development of low-grade peripheral inflammation in SCZ.
This study delineates the first systematic characterization of the gut microbiome and SCFA metabolic profiles in immune-activated subgroup of SCZ, and it reveals abnormal SCFA-mediated immunoregulatory responses in these patients. These findings provide new theoretical evidence for deepening the understanding of the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying immune activation in SCZ and for developing targeted precision therapeutic strategies.
The corresponding authors of the article are Professors Zhu Feng, Professor Ma Xiancang, and Associate Professor Zhang Jianbo from the School of Forensic Medicine of XJTU. The first authors are doctoral student He Xiaoyan and postdoctoral fellow Gao Yuan from the Department of Psychiatry, the FAH of XJTU.

Article Link: https://academic.oup.com/schizophreniabulletin/advance-article/doi/10.1093/schbul/sbaf110/8239456?login=true