The incidence of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) has been increasing in China. The main therapeutic drugs include aminosalicylic acid, glucocorticoids, immunosuppressants and biological agents. However, all these drugs have certain limitations, such as poor therapeutic efficacy and evident side effects, etc. Therefore, it is urgent to explore safer and more efficient new therapies.
To resolve this bottleneck issue, the team led by Professor He Shuixiang from Department of Gastroenterology of the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU) cooperated with relevant experts from Duke University, Chongqing University and Northwestern Polytechnical University to develop an efficient, specific and safe nano-carbon monoxide (CO) treatment system with reactive oxygen species, starting from the microenvironment characteristics of unbalanced M1/M2 polarization of intestinal macrophages and abnormal continuous activation of intestinal mucosal immune response in IBD. Using layer-by-layer self-assembly technology, chitosan/sodium alginate (Chi/Alg) polyelectrolyte multilayer film was constructed on the surface of mesoporous poly-dopamine nanoparticles loaded with CO prodrug, which is the key to endow nanoparticles with high stability, active targeting and good controlled release. The Chi/Alg barrier layer can effectively protect the loaded drugs from being destroyed by physical and chemical factors in the gastrointestinal tract, and the negatively-charged surface of nanoparticles is targeted to inflammatory colon tissues with positive surface through electrostatic interaction. Specifically enriched in the target site, Chi/Alg "nano-valve" is degraded under the stimulation of excessive oxidative stress signal in the lesion area, and CO is released responsively, which plays a role in anti-oxidative stress, regulating local immune response in the intestine and regulating intestinal microecology, providing a new therapeutic strategy for IBD.
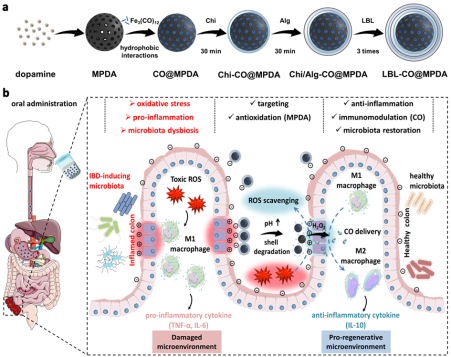
The above results are reported in an article entitled "An Orally-Administered Nanotherapeutics with Carbon Monoxide Supplying for Inflammatory Bowel Disease Therapy by Scavenging Oxidative Stress and Restoring Gut Immune Homeostasis" published in ACS Nano, an international authoritative journal in related field (IF: 17.1). Zhang Xu, a doctoral student from Department of Gastroenterology of the FAH of XJTU and Professor Yuan Zhang from Northwestern Polytechnical University are co-first authors. Professor He Shuixiang, Professor Cai Kaiyong from Chongqing University and Professor Yuan Zhang from Northwestern Polytechnical University are co-corresponding authors. The FAH of XJTU is the first and corresponding affiliation of this article.
