Recently, Professor Wang Qiang's team from Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi 'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) published an online article entitled "Label-free in vivo assessment of brain mitochondrial redox states during the development of diabetic cognitive impairment using Raman spectroscopy" in Free Radical Biology and Medicine, a prestigious journal worldwide, illustrating the latest research results of early diagnosis and treatment of diabetes-associated cognitive dysfunction (DACD). In this study, resonance Raman spectroscopy, an "optical fingerprint" tool, was first used to successfully monitor mitochondrial redox imbalance in the brain during the incidence and development of DACD in vivo, providing a novel indicator and monitoring tool for early identification of DACD.

Professor Wang Qiang's team used resonance Raman spectroscopy, an "optical fingerprint" tool, to study the mitochondrial redox state and successfully established corresponding algorithms, creating groundbreaking achievements in the assessment of brain mitochondrial redox imbalance during the incidence and development of DACD in vivo.
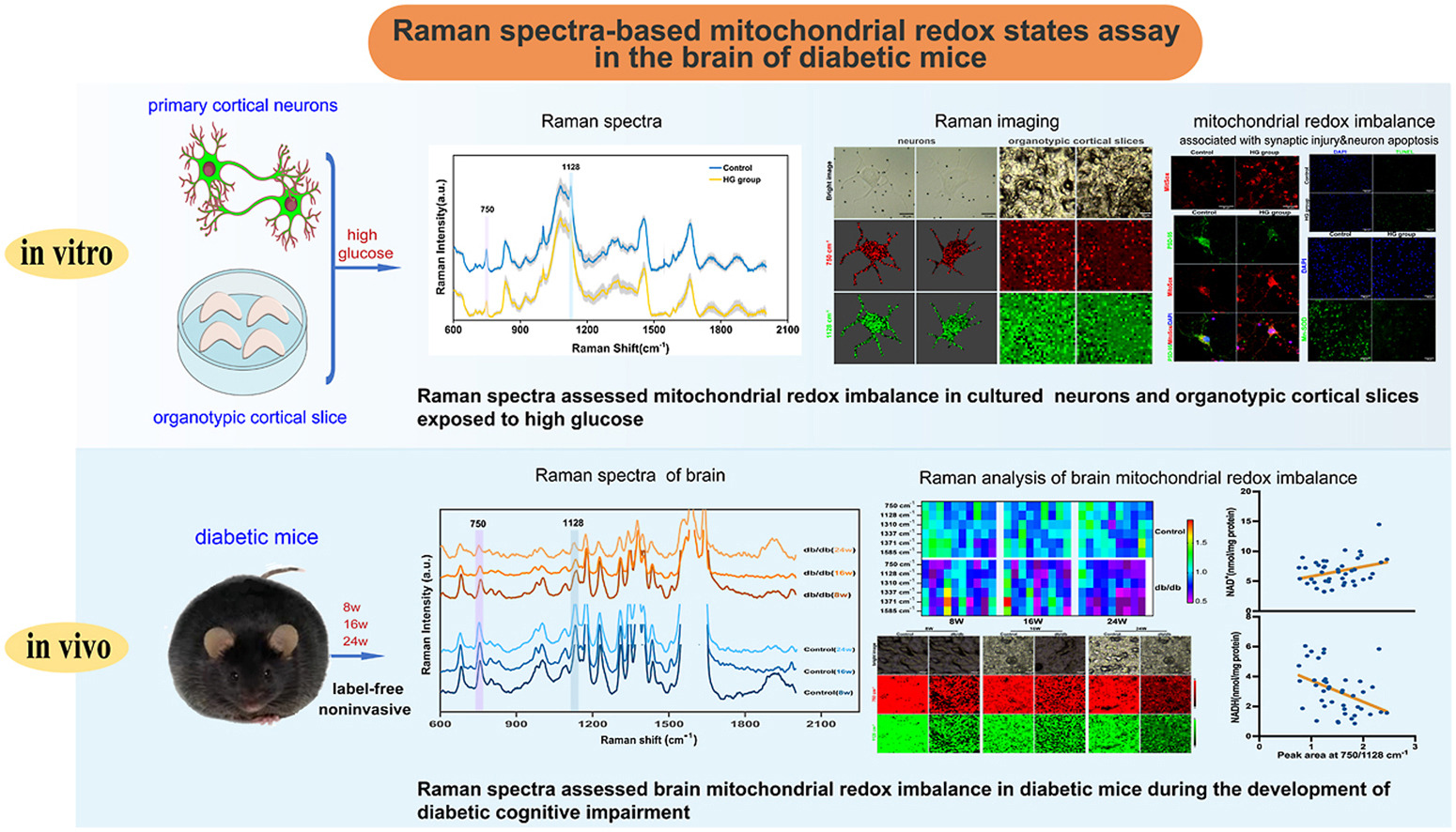
In this study, resonance Raman spectroscopy was firstly utilized to study mitochondrial redox imbalance in cultured neurons, organotypic slices and diabetic mice’s brain. Meantime, mitochondrial redox imbalance was associated with synaptic injury and neuron apoptosis. It is also the first study to use resonance Raman spectroscopy to assess mitochondrial redox imbalance during the incidence and development of DACD in vivo. The findings suggested that mitochondrial redox imbalance in cultured neurons and organotypic slices exposed to high glucose can be quantified by the reduction of Raman peak area at 750 cm-1 and 1128 cm-1, which were also associated with synaptic injury and neuronal apoptosis. Raman peak area at 750 cm-1 and 1128 cm-1 were also decreased in db/db mice aged 8, 16 and 24 weeks, and had a high correlation with the mitochondrial NAD+/NADH redox couple.
Based on successful assessment of the changes of mitochondrial redox state in diabetic mice’s brain at different weeks by resonance Raman spectroscopy in combination with evaluation results of DACD, mitochondrial redox imbalance in the brain occurred before measurable cognitive decline in 8-week-olddb/db diabetic mice, and might signal impending DACD. This achievement contributes to formulating corresponding early intervention and treatment, providing a novel technical approach and strategy for the progression of DACD. It is expected to realize early risk stratification and timely intervention and treatment, which is of significance for the study of other diabetes-associated complications.
This study was supported by Surface Project of National Natural Science Foundation of China and Industry Innovation Chain Project of Shaanxi Provincial Key Research and Development Program.
Article link:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0891584922001009?via%3Dihub