At present, surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies for malignant tumors. The tumor resistance to radiotherapy is the key factor restricting the efficacy of radiotherapy. How to improve the radiosensitivity is one of the persistent challenges of radiotherapy for tumors.

To resolve this challenge, the team led by Professor Han Suxia from Department of Radiation Oncology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi 'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) cooperated with the team of research professor Zhang Mingzhen from School of Basic Medical Sciences (Institute of Translational Medicine) of Institute of Medical Engineering to design a biomimetic nanoplatform based on hollow polydopamine nanoparticles through the strategy of chelation competition-induced polymerization (CCIP). The biomimetic nanoplatform integrates ultra-small platinum (Pt) nanoparticles, showcases catalase-like activity, catalyzes endogenousH2O2toO2, and relieves hypoxia tumor microenvironment (TME). The biomimetic nanoplatform has both mesoporous shell and large cavity structure, which can efficiently support Apoptin100-109(AP) and Verteporfin (VP) (AVPt@HP@M). Under X-ray irradiation, AVPt@HP@M can relieve hypoxia (Pt), promote apoptosis of tumor cells (AP) and X-ray-induced photodynamic therapy (X-PDT)(VP) can enhance the radiotherapy of colon cancer. The biomimeticnanoplatform possesses high biological safety, provides a novel strategy for effective radiosensitization, and has scientific significance and clinical reference value.
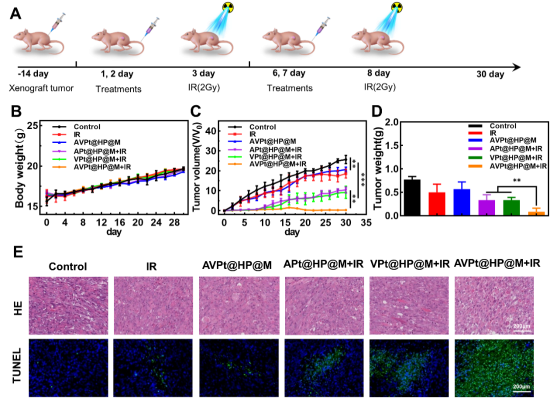
These research results have been published in an article entitled "All-in-one biomimetic nanoplatform based on hollow polydopamine nanoparticles for synergistically enhanced radiotherapy of colon cancer" inSmall, an authoritative journal in the field of materials, with an impact factor of 13.28.
Doctoral student Gong Liuyun from Department of Radiation Oncology of the First Affiliated Hospital of XJTU is the first author, and Professor Han Suxia and research professor Zhang Mingzhen are co-corresponding authors of this article. This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, Top Young Talents Program of XJTU and other projects. Instrumental Analysis Center and Biomedical Experimental Center of XJTU provided characterization testing support for this study.
DOI:10.1002/smll.202107656