On December 15, 2021, the latest achievement titledCerebrospinal fluid from healthy pregnant women does not harbor a detectable microbial communitywas online publishedinMicrobiology Spectrum(IF 7.171) affiliated to American Society for Microbiology in the form of research article, which is the result of cooperative studyby Prof. Ye Kai’s team from the Single Cell Sequencing Platform of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University(XJTU)and Prof. Zhao Gang’s research team, who is the Dean of Northwest UniversitySchool of Medicine and chief physician of Department of Neurology, Xijing Hospital.

It has been founded that microorganisms are colonized in human intestinal tract, oral cavity, skin, obstetric canal, lung and more as a biome with huge quantity and great varieties. However, there have been disputes on whether microorganisms exist in the placenta, amniotic fluid or blood in healthy persons, due to both collection challenges of control samples in the experiment design and the influence of identification and traceability of contaminants during the data analysis on the conclusion. Cerebrospinal fluid circulating in the central nervous system is generally considered sterile because of effective protection of blood brain barriers. However, this conclusion has been challenged by many researches. An example is that porphyromonasgingivalis from the oral cavity was identified in the brain in the patients with Alzheimer’s disease. DNA virus was found in a study of cerebrospinal fluid samples in few healthy subjects. No exact conclusion has been drawn on whether the microorganisms in these sites are colonized or accidental, though current methodologies have been greatly improved in terms of experiment and computation.
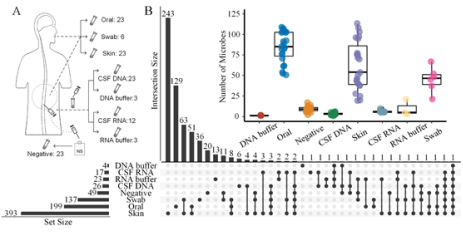
For this purpose, in the collection of cerebrospinal fluid samplesin 23 healthy pregnant women from Xijing Hospital, the collaborative team collected oral cavity and skin samples as positive control group with normal saline used as the negative control group, and sterile swabs and reagents used during the extraction were designed as potential contamination control group. These samples were given the metagenomics sequencing. To evaluate the activity of potential microorganisms, metagenomics sequencing was carried out for 12 cerebrospinal fluid samples. According to the data analysis, no evidence indicated microorganisms were colonized in cerebrospinal fluid samples, and the species detected may come from the control or contamination.
The first author of this article is Kang Yongyong, researcher of Single Cell Sequencing Platform of the First Affiliated Hospital of XJTU, and co-first authors are Dr. Ji Xinchao from Xi’an No. 3 Hospital, Prof. Guo Li (now work in Peking University Institute of Advanced Agricultural Sciences) and doctorial student Xia Han from School of Automation Science and Engineering,XJTU. The corresponding authors are Prof. Ye Kai, the head of Single Cell Sequencing Platform from School of Automation Science and Engineering,XJTUand the First Affiliated Hospital of XJTUand Prof. Zhao Gang from Northwest University School of Medicine and chief physician of Department of Neurology, Xijing Hospital. The first signature unit is the First Affiliated Hospital of XJTU.
This research is funded by National Key Research and Development Program and National Natural Science Foundation of China and more.
Access to this article by the link:https://journals.asm.org/doi/10.1128/Spectrum.00769-21

Ye Kai, professor and doctoral advisor, is the winner of National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars. He now is the chief scientist in XJTUInformation and Biomedicine Crossing Center and head of Single Cell Sequencing Platform of the First Affiliated Hospital and Med-X Research Institute-Centerof Digital Medicine. Prof. Ye has been devoted to the research of bioinformatics with the mission to build a multi-disciplinary cross-scientific research platform, cultivate multi-disciplinary talents and make his contributions to “bottleneck” problems in the precision medicine, green biomanufacturing and other frontier crossing fields. Prof. Ye Kai has published more than 70 articles inScience, Nature, Nat Med, Nat Communand other journals. Of those, there are 14 ESI papers highly cited, 1 hot paper and more than 22,000 citations in others’ SCI papers.
Brief introduction of Single Cell Sequencing Platform
The Single Cell Sequencing Platform of the First Affiliated Hospital of XJTUaims to provide single cell sequencing services for cooperative teams inside and outside of the hospital, give technical support for the fast development of relevant disciplines with single cell sequencing technology advantages and then promote personalized diagnosis and treatment and precision medicine of our hospital. Using artificial intelligence, biomedicineand omics data analysis methods and in the research direction of clinical medicine big data mining and application,the Center of Digital Medicine that has beenestablished recently works on the development of life medicine big data analysis and genetic mutation detection algorithms for major diseases in XJTU. The team embraces the engagement of scholars in the information, biology, medicine and other cross-disciplines. If you have the intention, please contact with Mr. Hai:haijing@xjtu.edu.cn.