On January 29, the Journal Cellular & Molecular Immunology published the latest research results of the team led by Professor Shi Bingyin from the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi 'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) in an online article entitled "A novel CD4+CTL subtype characterized by chemotaxis and inflammation is involved in the pathology of Graves' orbitopathy". This is another significant original outcome since the first relevant article published in Clinical and Translational Medicine in November, 2020.

In the present study, the pivotal role of CD4+ T lymphocyte subsets with chemotactic and inflammatory characteristics in the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy was confirmed for the first time around the globe. Professor Shi Bingyin's team applied single-cell sequencing assay to comprehensively analyze the CD4+T lymphocytes in peripheral blood of Graves’ orbitopathy patients, and found that CD4+CTL subsets plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy and is intimately associated the efficacy of hormone shock. Meantime, these cell subsets are characterized with remarkable clone expansion and thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor specificity. This achievement has made a further breakthrough in unravelling the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy.
This study was jointly completed by the team led by Professor Shi Bingyin from Department of Endocrinology of our hospital and the team led by Professor Ye Kai from Department of Telecommunications of XJTU. The First Affiliated Hospital of XJTU is the first affiliation of this article. Dr. Wang Yue and Doctoral student Chen Ziyi from Department of Endocrinology of our hospital, and Doctoral student Wang Tingjie from Key Laboratory of Intelligent Network and Network Security of Ministry of Education, School of Telecommunications of XJTU are the co-first authors. Professor Shi Bingyin is the corresponding author, and Professor Ye Kai is the co-corresponding author of this article.
Graves’ orbitopathy is an irreversible disease with poor clinical efficacy, which significantly affects the survival and quality of life of patients. In this study, single-cell RNA sequencing technology was applied to elucidate the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy, aiming to explore novel diagnostic and therapeutic targets. Single-cell RNA sequencing assay can analyze the genome from the single-cell level, which applies gene sequencing to the single-cell level and plays a crucial role in identifying the type and function of cells, and the changes and variations of specific cell health or state.
In the present investigation, the CD4+ T cells were sorted from treatment-naïvehyperthyroidism patients and Graves’ orbitopathy patients who were not given with hormone pulse therapy and then subject to single-cell sequencing assay. The t-SNE algorithm analysis of single-cell RNA sequencing data revealed that CD4+ T cells collected from hyperthyroidism and Graves’ orbitopathy patients can be divided into six cell types (CT). Among them, CT6 is characterized with Graves’ orbitopathy specificity and widely expresses KLRG1, GZMB, PRF1, CX3CR1, CCl4, CCL5 and IFNG, indicating that CT6 simultaneously possesses cytotoxicity, inflammation and chemotaxis. T cell receptor sequencing demonstrated that compared with the initial CD4+T cells, the diversity of CD4+CTL in patients with Graves’ orbitopathy is significantly decreased, and significant oligoclonal expansion is observed. The findings in this study also revealed that CD4+CTL can be significantly activated and toxic molecules can be released after stimulated by thyrotropin receptor, an autoantigen of Graves’ orbitopathy. Taken together, CD4+CTL plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy, which features significant clone expansion and thyroid-stimulating hormone receptor specificity.
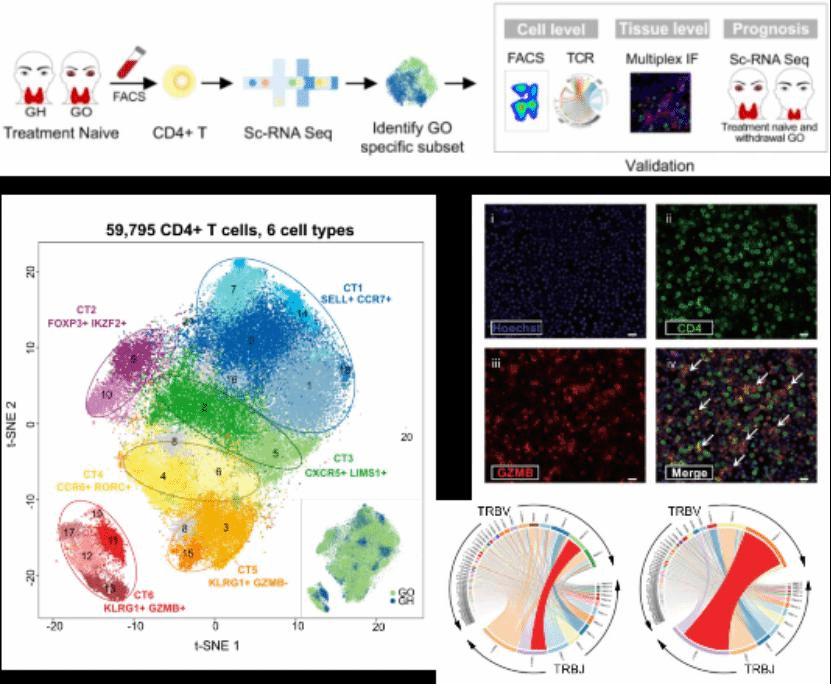
The discovery of the important role of CD4+CTL in the pathogenesis of Graves’ orbitopathy provides a novel direction for the prevention, treatment and prognosis of Graves’ orbitopathy. Professor Shi Bingyin's team will focus on the specific functions of CD4+CTL in the incidence and progression of Graves’ orbitopathy in subsequent investigations, and actively develop targeted therapeutic methods for CD4+CTL subsets, providing more efficacious approaches for the prevention and treatment of Graves’ orbitopathy.
Article link:
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41423-020-00615-2
https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ctm2.218