Recently, the team led by Professor Zhu Yaomin from the Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU), in collaboration with the team of Assistant Researcher Wang Ruiduo from the Xi’an Institute of Optics and Precision Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, has made a breakthrough in the trace detection of fructose in serum. The related research findings have been published in the international top journal in the field of biosensors, Biosensors and Bioelectronics, under the title “Advanced Surface-Functionalized Optical Fiber Biosensing Platform for Ultrasensitive Fructose Quantification in Biological Fluids”.
The blood concentration of fructose is closely associated with a variety of metabolic diseases such as type 2 diabetes and fatty liver; however, rapid, sensitive and low-cost quantitative analysis of fructose in clinical practice has long been a challenge, constrained by factors such as complex sample processing and long detection cycles.
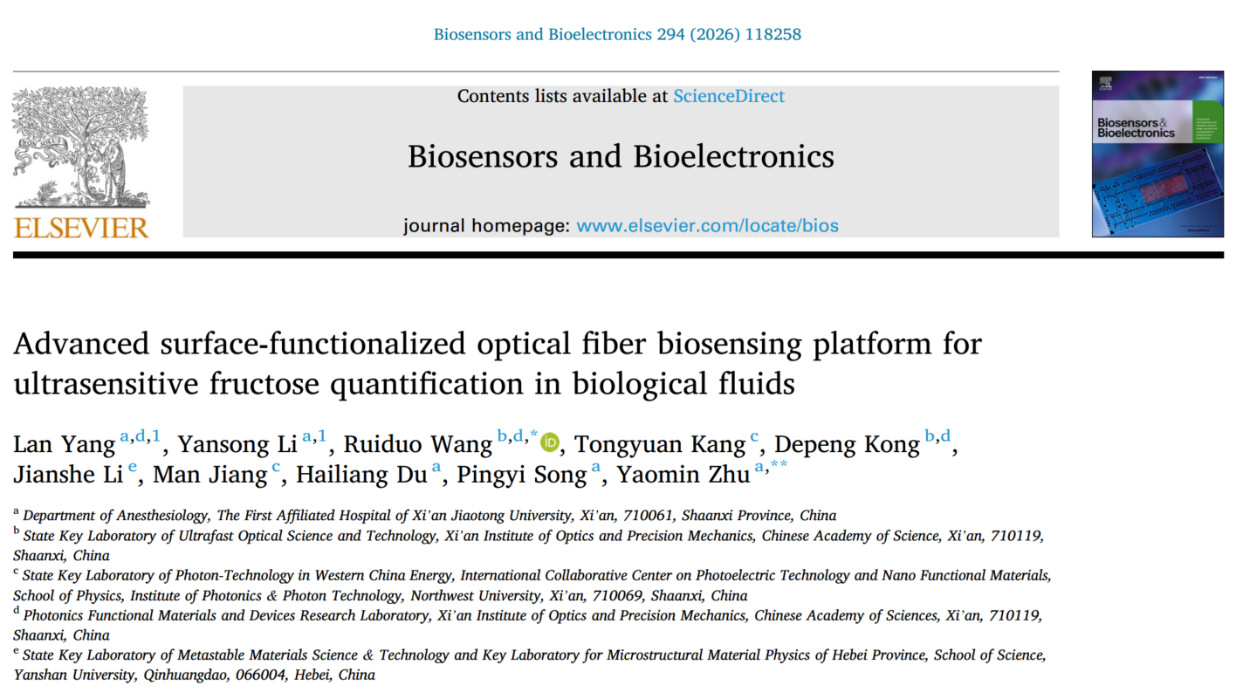
To address this clinical need, the research team innovatively integrated optical fiber sensing technology with biomolecular recognition mechanisms and developed an optical fiber biosensor based on a cascaded structure. In this sensor, a microsphere resonant cavity is constructed by splicing a single-mode fiber with a seven-core fiber, and a thermally fused tapered structure is used to enhance the refractive-index response. Ketohexokinase is then covalently immobilized on the fiber surface to form a specific recognition layer, enabling targeted capture of fructose. Combined with a microfluidic cyclic solution-exchange cleaning system, the sensor achieves both high sensitivity and reusability.
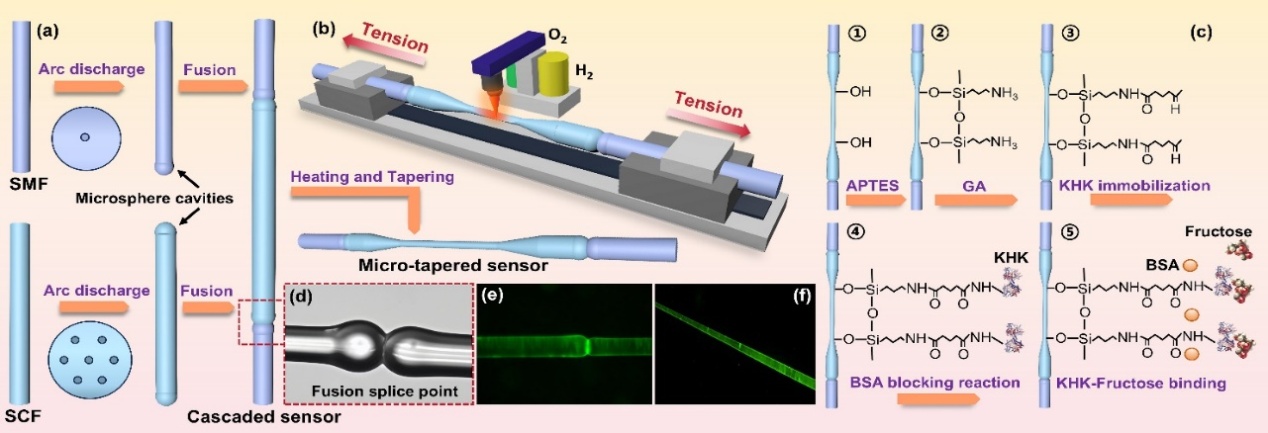
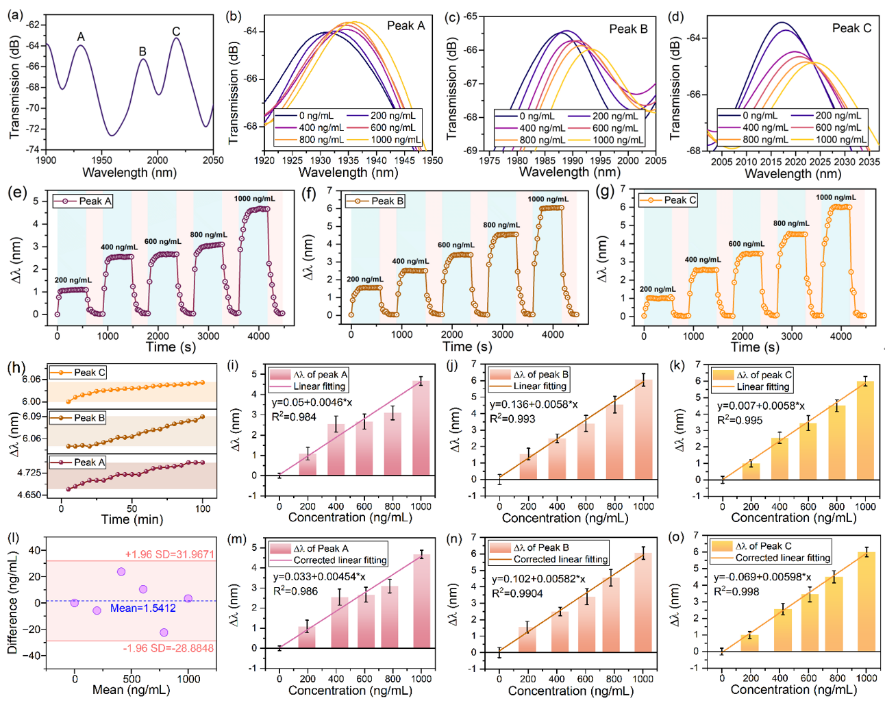
Performance testing shows that the sensor exhibits a dynamic detection sensitivity of 5.98 nm/(μg/mL) for fructose standards, with a limit of detection as low as 12.6 ng/mL. To ensure accuracy, the research team calibrated the samples using the gold-standard method of high-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (LC-MS), and Bland-Altman analysis confirmed that the sensor readouts are in excellent agreement with the LC-MS results. The assay time for a single sample is only 5 minutes, and the system demonstrates outstanding anti-interference capability and specificity, with its overall performance reaching the international leading level.
Testing with clinical serum samples has demonstrated that this technology enables precise quantification of fructose concentrations and establishes a new optical fiber spectroscopic platform for biochemical molecular detection, providing critical support for the diagnosis, risk assessment and individualized treatment of metabolic diseases and helping to optimize clinical decision-making. In addition, this sensor platform can be extended to the detection of other biomarkers or chemical compounds, injecting new momentum into clinical medical research.
Professor Zhu Yaomin is the last corresponding author of the paper, and doctoral candidate Yang Lan and Associate Researcher Li Yansong are co-first authors. This work represents another milestone achievement for the Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine in the field of medicine-engineering integration, following the translational development of a visual adjustable double-lumen tube.
Original article link:
Advanced surface-functionalized optical fiber biosensing platform for ultrasensitive fructose quantification in biological fluids - ScienceDirect