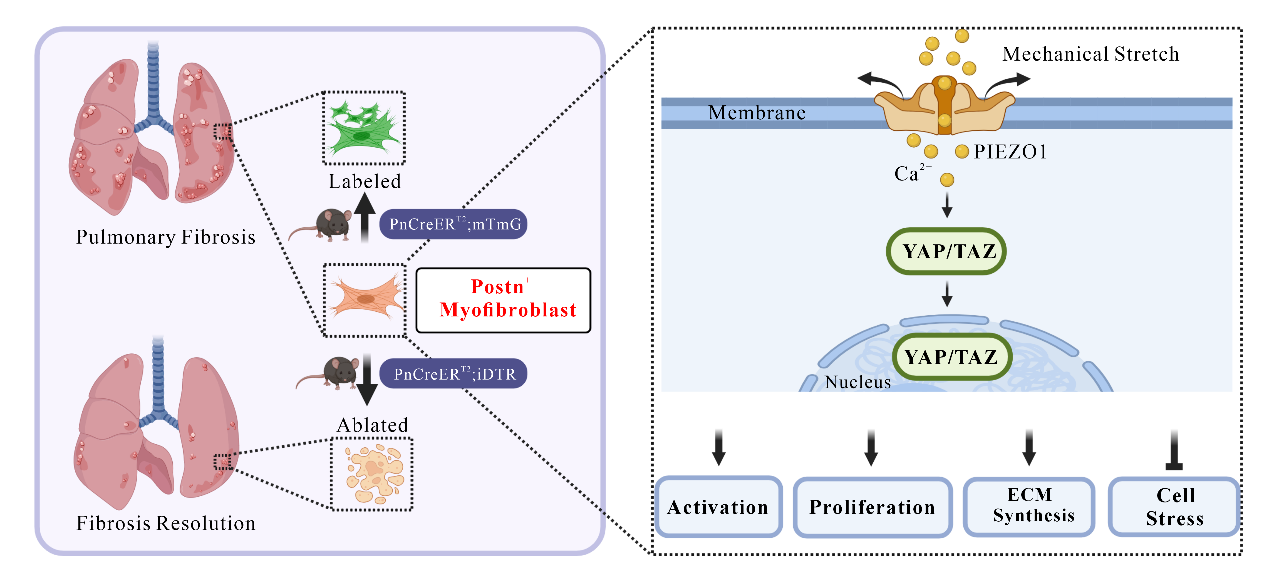
On June 2, 2025, the teams of Professor Wang Shengpeng, Professor Yuan Zuyi and Professor Yan Yang from the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) published a research article entitled "PIEZO1 mediates periostin+ myofibroblast activation and pulmonary fibrosis in mice" in the international authoritative journal of The Journal of Clinical Investigation (JCI). This study revealed for the first time that Periostin protein can be used as a specific marker of pulmonary myofibroblasts, and unraveled the molecular mechanism of PIEZO1, a mechanocensitive cation channel, that drives pulmonary fibrosis by regulating the activation of myofibroblasts, providing a novel drug target for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), a disease resembling cancer.

In this study, the teams independently developed Postn-CreERT2;mTmG tracing and Postn-CreERT2;iDTR mouse models. Experimental findings confirmed that periostin (Postn) is a marker of myofibroblasts after lung injury, and Postn+ myofibroblasts cover almost all activated myofibroblasts. Specific ablation of Postn+ myofibroblasts can significantly mitigate the degree of pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin in mice. Meantime, in the lung tissue of IPF patients, Postn+ myofibroblasts are abundantly expressed in the fibroblastic foci, highlighting the important clinical relevance of Postn markers in pulmonary fibrosis.
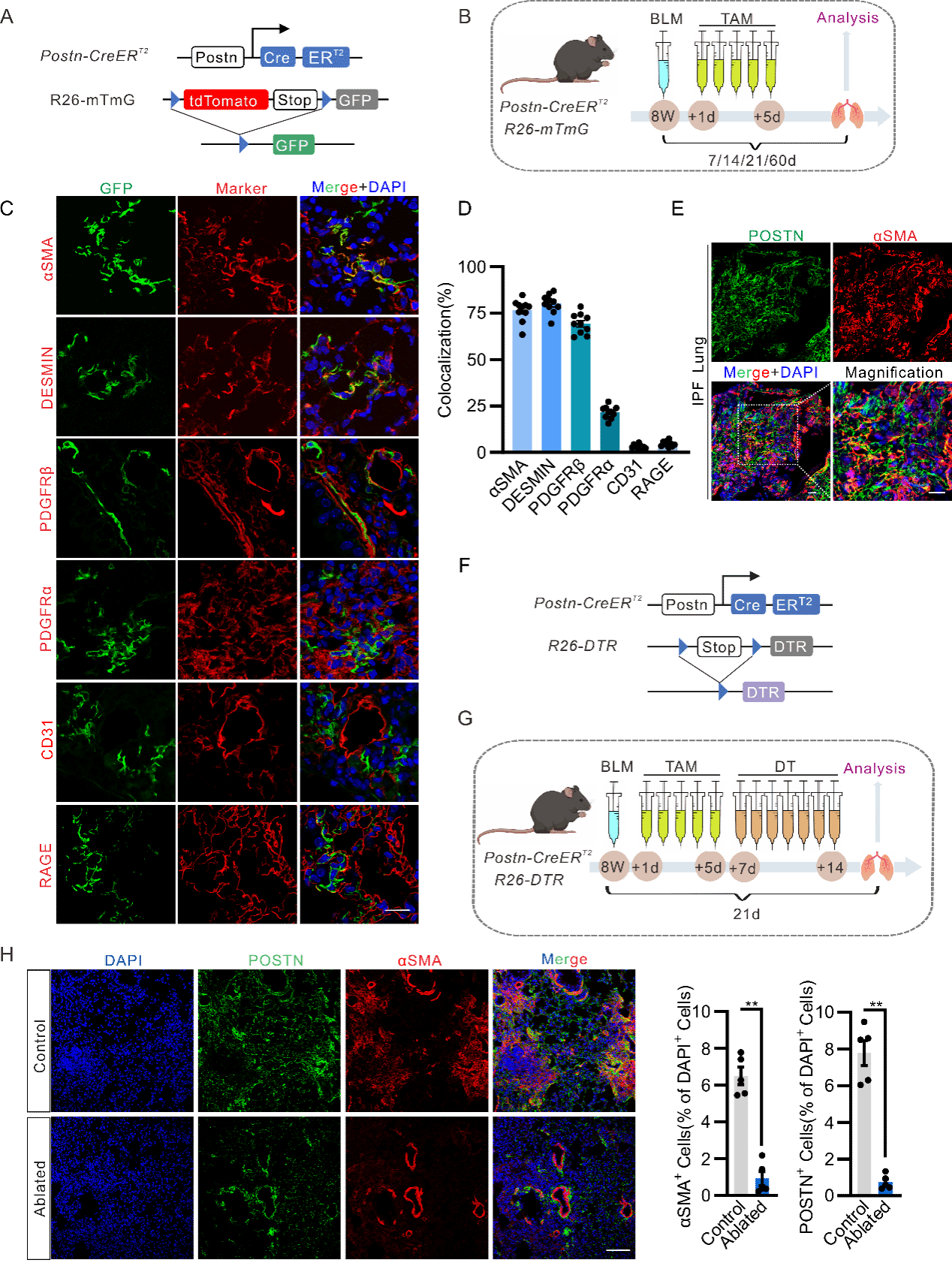
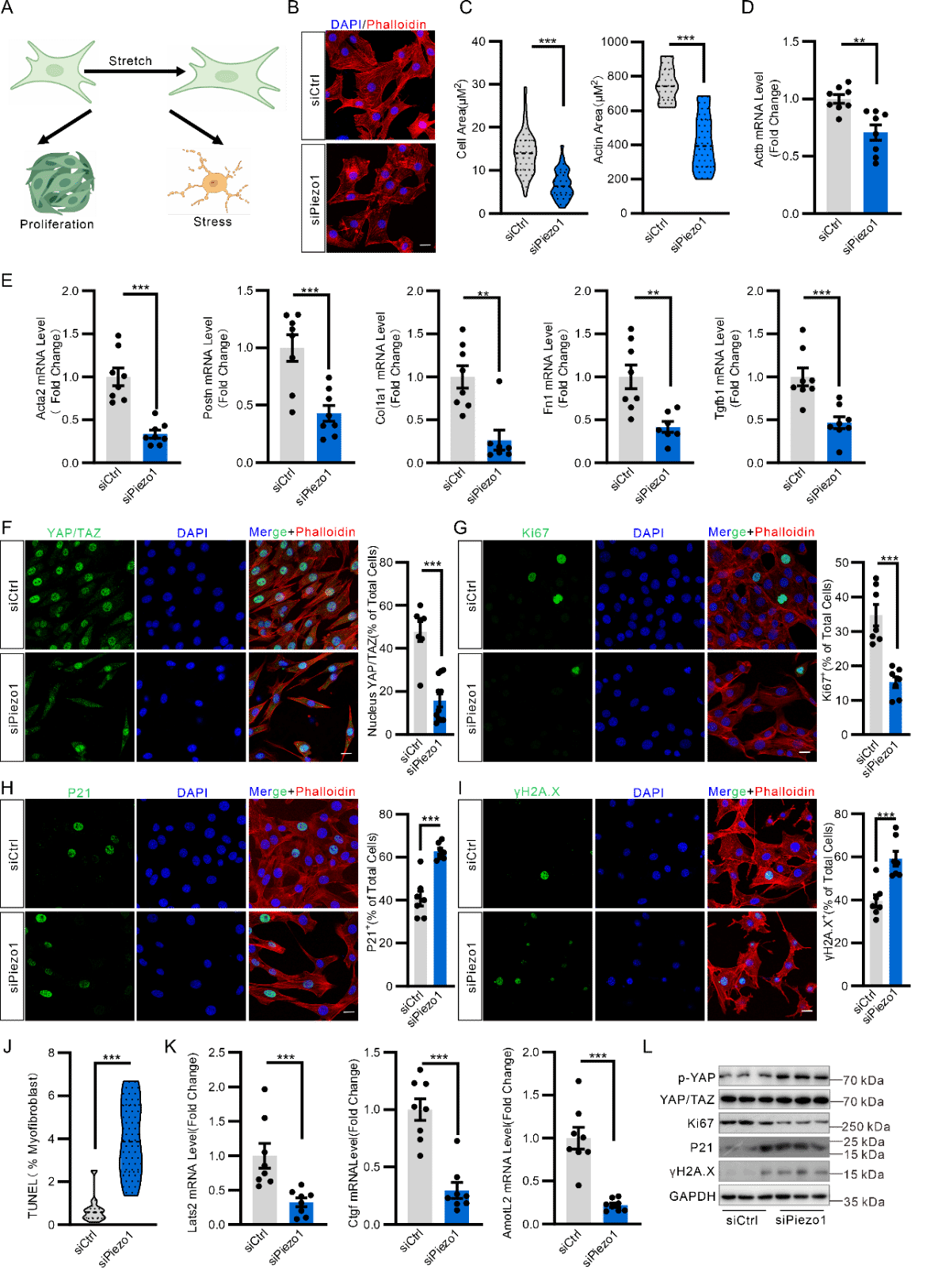
The teams also found that PIEZO1 is expressed and functional in Postn+ myofibroblasts. Experiments of Postn-Piezo1-KO mouse models and bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis models confirmed that specific knockdown of Piezo1 or inhibiting Piezo1 function in myofibroblasts can reduce pulmonary inflammatory reactions and mitigate the degree of pulmonary fibrosis. In vitro studies further indicated that PIEZO1 can promote the activation and proliferation of myofibroblasts, inhibit cellular apoptosis and accelerate the synthesis and secretion of extracellular matrix through the PIEZO1-RhoA/ROCK-YAP/TAZ signal axis.
PhD Xu Liran and Li Ting from FAH, Associate Professor Cao Yapeng from School of Basic Medicine, and postdoctoral fellow He Yu from FAH are co-first authors. Professor Wang Shengpeng, Professor Yuan Zuyi and Professor Yan Yang are co-corresponding authors of this article. This study provides a novel direction for unraveling the pathogenesis of IPF from a mechanical perspective, which is expected to revolutionize the therapeutics of pulmonary fibrosis.
Full-text link: https://www.jci.org/articles/view/184158/pdf