Recently, the bone tumor surgery team led by Professor Han Xuezhe from Department of Orthopedics of the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi 'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) took the lead in applying minimally invasive co-ablation under O-arm navigation to relieve the pain and prevent tumor progression in a patient with malignant sacral metastases.
A 67-year-old female patient was diagnosed with renal clear cell carcinoma three years ago, and developed recurrent pain in the left lumbosacral region six months ago. Concurrent radiochemotherapy yielded poor efficacy. Professor Han Xuezhe from Department of Orthopedics and Professor Bian Weiguo conducted comprehensive physical examination and imaging result analysis for the patient. The possibility of sacral metastasis from renal cancer was considered, and surgical resection was recommended. Nevertheless, her physical condition was ineligible for traditional surgery. Percutaneous co-ablation is a minimally invasive procedure, and tumor tissues can be rapidly cooled to -196℃ intraoperatively, forming ice crystals within tumor cells, leading to dehydration and rupture of tumor cells in the tissues, destroying small vessels in the tumor, and inducing ischemia and hypoxia. Subsequently, the temperature was immediately increased up to 80℃ , which can further kill tumor cells, mitigate bleeding, prevent cancer cell implantation and metastasis and exert high analgesic effect. However, the sacral vertebra is adjacent to the sacral nerve root, and tumor ablation may damage the nerve root. The morphology of sacrum is complex and irregular, and conventional C-arm fluoroscopy yields poor effect. After repeated consultation among team members of Professor Han Xuezhe and Professor Bian Weiguo, O-arm navigation was adopted to achieve precise and targeted ablation under real-time guidance, which can avoid nerve root injury under intraoperative neurophysiological monitoring throughout the procedures.
On the day of surgery, with tremendous support and cooperation from Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, the team applied O-arm real-time navigation to accurately pinpoint the location of lesions and nerve roots, avoid key nerves and vessels, and establish surgical channels. Initially, the temperature of ablation needle was lowered to -196℃ for several minutes, and then the temperature was rapidly elevated to 80℃ for thermal ablation. Co-ablation could kill local tumor cells, relieve pain and stimulate systemic tumor immunity. Throughout the surgery, no abnormal change was observed by electrophysiological monitoring. Postoperatively, the pain symptoms were significantly relieved. The patient reported no abnormal changes in muscle strength and skin sensation of the lower limbs.
Co-ablation technology has been applied in the treatment of liver cancer, lung cancer and malignant soft tissue tumors and achieved favorable efficacy in China. This is the first case of successfully applying co-ablation technology in treatment of sacral metastatic tumors, which resolves the constraints of applying this technology in spinal tumors, paves the way for diverse and qualified treatment for patients with spinal tumors, and better serves patients with bone tumors.
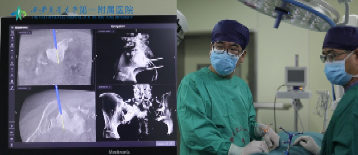
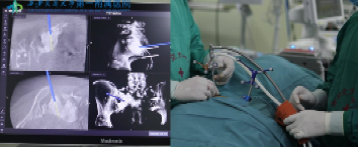
Precise intraoperative positioning by using O-arm navigation system