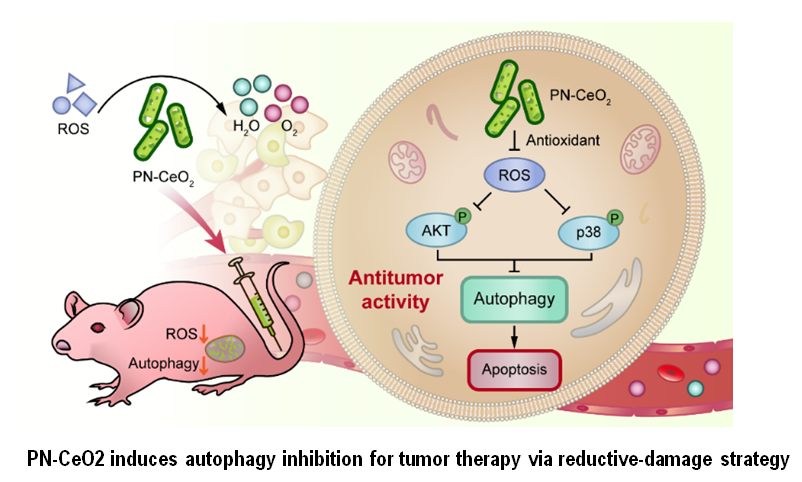
In recent years, significant challenges exist in anti-tumor therapy through autophagy inhibition. To resolve this problem, the team led by Professor Zheng Yan from Department of Dermatology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi 'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) cooperated with the team of Professor Qu Yongquan from School of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering of Northwestern Polytechnical University to demonstrate a reductive-damage strategy to enable tumor therapy by the inhibition of protective autophagy via the catalytic scavenging of ROS using porous nanorods of ceria (PN-CeO2) nanozymes as autophagy inhibitor, which is synthesized by two-step hydrothermal approach. Recently, these research results were published in Nano Research as a research article entitled "Reductive damage induced autophagy inhibition for tumor therapy". The impact factor of Nano Research in 2021 was 10.269, classified in JCR Area 1 in multiple fields, such as nano science, nanotechnology, applied physics, chemistry, physics, material science and multi-discipline,etc.

The morphology and size of PN-CeO2were characterized by transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy dispersive spectromete (EDS), X-ray diffractometer (XRD) and X-ray photoelectron spectrometry (XPS). The superoxide dismutase (SOD)- and catalase (CAT)-like activities of PN-CeO2 were evaluatedin vitroto verify its antioxidant activity. Furthermore, skin squamous cell carcinoma (cSCC) with high autophagy level was chosen as a tumor cell model. The antitumor activity, signaling pathway and biological safety of PN-CeO2 were systematically evaluated both in vivo and in vitro. The results demonstrate that PN-CeO2 nanoenzyms, as an autophagy inhibitor, can effectively catalyze intratumoral ROS degradation via its specific antioxidant enzyme mimic activity, and further inhibit the activation of PI3K/AKT and p38MAPK pathways in cSCC to suppress protective autophagy and activate cell apoptosis, thereby achieving highly-efficient antineoplastic effect. In addition, the findings in this study emphasized that compared with HCQ with significant toxicity, PN-CeO2 is a safe and effective anti-tumor autophagy inhibitor. Taken together, a reductive-damage strategy was proposed to enable tumor therapy by the inhibition of protective autophagy via the catalytic scavenging of ROS using PN-CeO2 nanozymes as autophagy inhibitor, providing a novel and promising anti-tumor therapeutic approach.
The First Affiliated Hospital of XJTU is the first and corresponding affiliation. Professor Zheng Yan, Professor Qu Yongquan and PhD Tian Zhimin from Northwestern Polytechnical University are the co-corresponding authors. Doctoral students Wang Yuqian and Huang Yingjian are the co-first authors of this article.
Article link:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12274-022-5139-z