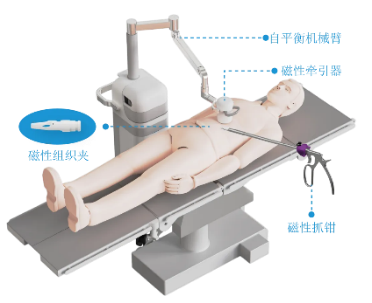
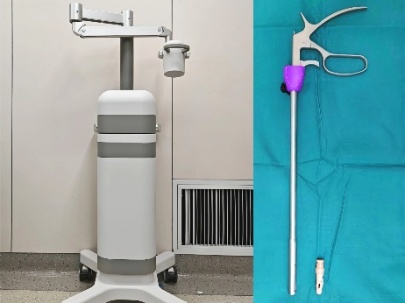
The pediatric surgery team at the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU) is the first in China to apply magnetic surgery technology to pediatric surgical care, offering children, under the concept of “Scarless Love”, a new treatment option with less trauma and faster recovery, and ushering pediatric surgery into a new era of precision operations. The core of magnetic surgery technology has two principal directions: The first is magnetic compression technology, which is applicable to reconstructing physiological lumens such as the esophagus, biliary tract, and intestine. Traditional anastomosis requires sutures or titanium staples that penetrate tissue and can easily lead to complications such as leakage and infection; this technique relies on sustained magnetic attraction to continuously compress the tissue, causing necrotic tissue in the middle to slough while surrounding tissue regenerates and fuses, forming a sutureless anastomosis. It enables individualized treatment and has been used for conditions such as congenital esophageal atresia and choledochal cysts. The second is magnetic anchoring technology, which addresses the problem of needing to make multiple “holes” in endoscopic surgery by using magnetic attraction to achieve non-contact anchoring; without additional ports, the surgeon manipulates an anchoring magnet to control the target magnet, expose the operative field, and reduce chest and abdominal wall penetration injuries, and it has been applied to procedures such as laparoscopic appendectomy and resection of intra-abdominal and retroperitoneal tumors.
In clinical practice, the team has achieved multiple breakthroughs: A world-first thoracoscopic magnetic anastomosis for esophageal atresia, which is minimally invasive, safe, and effective; a dual-scope combined endoscopic magnetic compression procedure that successfully recanalized the esophagus of a child with traumatic esophageal atresia after over five years and more than twenty surgeries without healing; a laparoscopic cardioplasty with magnetic anastomosis that reduces tissue injury and preserves cardia function; a laparoscopic magnetic bilioenteric anastomosis that provides a new pathway for biliary-enteric reconstruction in children; and magnetic-traction two-port laparoscopic appendectomy as well as single-port laparoscopic resection of retroperitoneal tumors, both of which reduce abdominal-wall punctures and injury while balancing efficacy and cosmesis.
Magnetic surgery technology offers marked advantages in pediatric surgery. It is ultra-minimally invasive, often implanting magnets via endoscopy or small incisions, leaving no large scars and meeting children’s aesthetic needs; it substantially reduces discomfort, with mild postoperative pain; it accelerates recovery, shortens hospital stay, and lessens the impact on growth and schooling; its stable and controllable magnetic forces reduce complications associated with conventional surgery; it can also address complex challenges that are difficult for traditional procedures, such as deep or long-segment tissue defects.
Magnetic surgery technology delivers maximal health benefits for children with minimal trauma, injects innovative momentum into the development of pediatric surgery, and safeguards children’s lives and health.