Recently, the team of Professor Lei Xinjun, the expert stationed at the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) and director of Department of Cardiology of Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital cooperated with Professor Xie Dujiang, a member of Professor Chen Shaoliang’s team from Nanjing First Hospital, successfully carried out percutaneous pulmonary artery denervation (PADN) for a patient with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension, the first case in northwest China.
A 53-year-old male patient had chest tightness and shortness of breath after exercise 3 years ago, which were aggravated and complicated with cyanosis of mouth and lips 1 year ago. The patient was not effectively treated by targeted drugs, and developed decreased exercise endurance and poor heart function. Ultrasound showed the right atrial and right ventricular enlargement and severe pulmonary hypertension after the closure of atrial septal defect. Recently, the patient was admitted to Department of Cardiology of Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital for further treatment. Color Doppler ultrasound revealed abnormalities in multiple indexes.
After scientific diagnosis and comprehensive evaluation by Professor Lei Xinjun, Professor Xie Dujiang and other experts, it was determined to adopt percutaneous pulmonary artery denervation (PADN), the cutting-edge treatment in this field. PADN is a percutaneous pulmonary artery interventional therapy, which uses a specific catheter to transmit radio-frequency energy to the sympathetic nerve of the adventitia of the pulmonary artery, leading to absence of the myelin sheath and the fusion of axons, thereby inhibiting sympathetic nerve activity, dilating pulmonary artery, increasing cardiac output, reducing pulmonary artery pressure, inhibiting pathological remodeling of pulmonary artery and improving patients' exercise endurance and cardiac function, and eventually achieving the effect of "one-time minimally invasive procedure for long-term benefit".

The team consisting of Professor Lei Xinjun, Professor Xie Dujiang, Professor Chen Xiuying from Qinghai Provincial People's Hospital and Professor Lin Rongxiang first performed the right heart catheterization and DSA of pulmonary arteries, and then selected the optimal mode of PADN ablation catheter based on anatomical characteristics of CTA of pulmonary arteries.
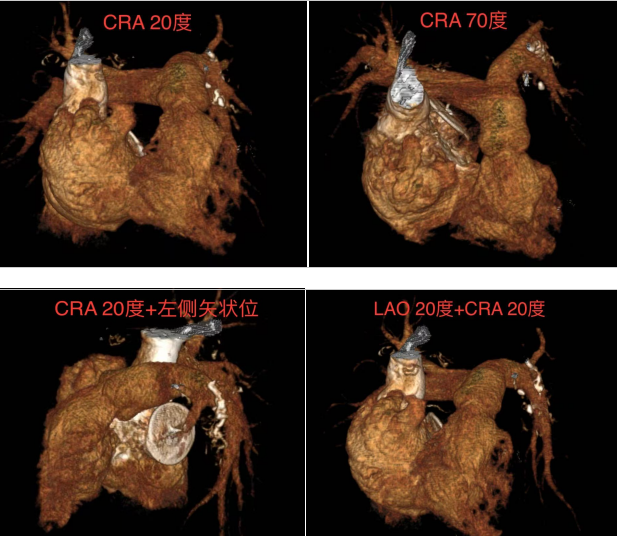
Under precise positioning, radiofrequency ablation was carried out for 4 targets, respectively. The 90-min operation was successfully completed. Intraoperatively, no significant discomfort was identified. Postoperatively, the right cardiac catheterization showed that the average pulmonary artery pressure was decreased by 12.5% and pulmonary vascular resistance was declined by 12.9% immediately after PADN. High surgical efficacy was achieved. Currently, the patient is recovering steadily.
