On July 19, 2024, Professor Wang Tuo’s team of neurological tumor group from Department of Neurosurgery of the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) utilized a novel hand-held cell microscope for the first time to complete immediate pathological diagnosis of complicated intracranial tumors.
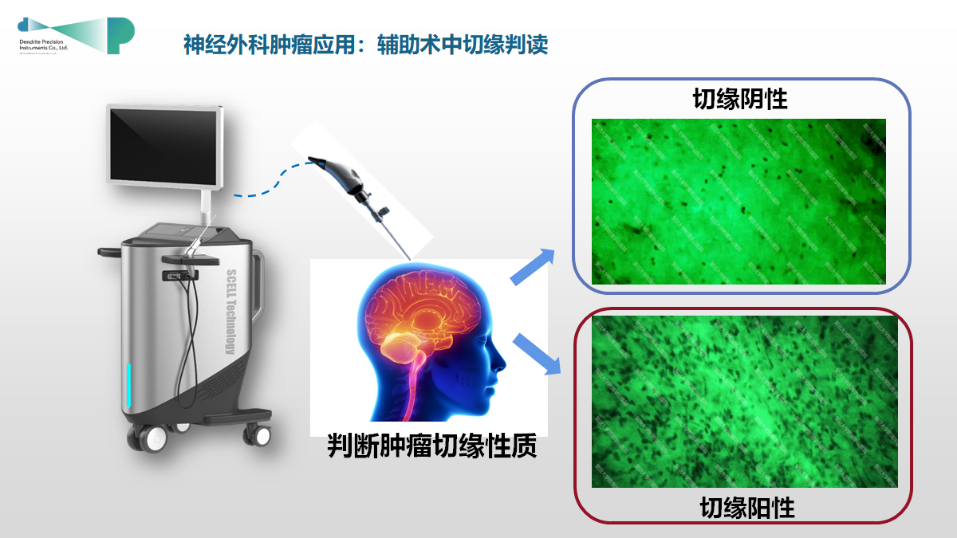
Schematic diagram of hand-held cell microscope
A 65-year-old male patient reported chief complaints of dizziness and unresponsiveness for more than 2 months. Cranial MRI showed space-occupying lesions in the left frontal lobe and the anterior horn of the lateral ventricle, and it was difficult to deliver differential diagnosis between glioma and lymphoma. He was admitted to Department of Hematology of FAH. Professor Li Jing proposed that the treatment regimens of these two types of tumors are completely different. Specifically, glioma should be radically resected and even the resection range should be extended to prolong the recurrence time, while lymphoma should be treated with bone marrow transplantation combined with CART treatment after being diagnosed according to pathological results. The patient's condition progressed rapidly. Hence, it was urgent to perform pathological diagnosis of the tumor nature, and it will take approximately two weeks to rely on conventional pathological examination, delaying the treatment opportunity.
After explicit preoperative multimodal MRI and MDT consultation, Professor Wang Tuo finally decided to adopt neurosurgery robot-assisted puncture biopsy combined with rapid fluorescent biopsy using intraoperative hand-held microscope. Pathological classification could be immediately determined intraoperatively, which provided sufficient evidence and assistance for subsequent treatment protocol. Intraoperatively, rice grain-sized lesion tissue was obtained by puncture. After fluorescein sodium and methylene blue staining, tumor cell structure was clearly visible (×1280 times). During the operation, a pathologist was invited for consultation and the diagnosis of lymphoma was confirmed. The diagnosis process only took 3 minutes, and the operation was successfully completed.
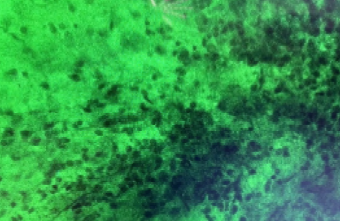
Tumor tissue photo taken by intraoperative hand-held cell microscope (×1280 times)
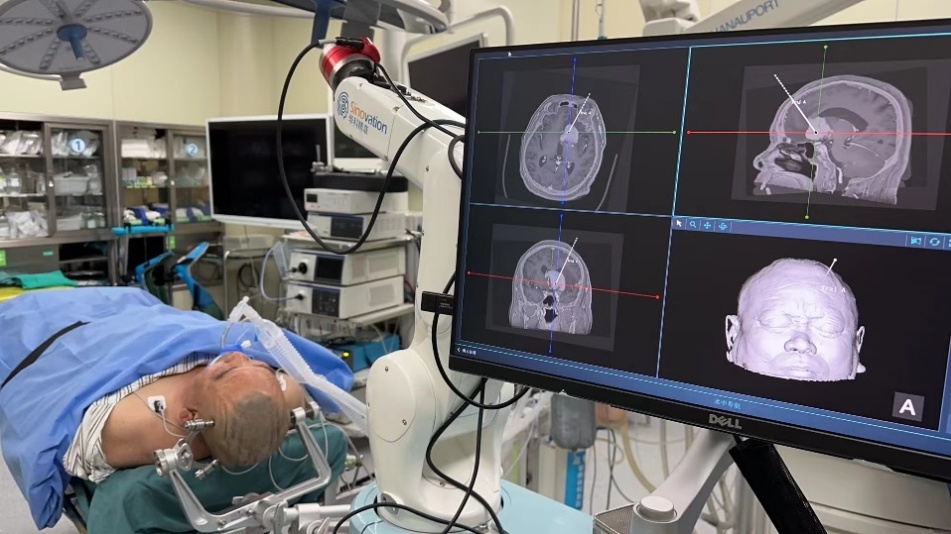
Robot-assisted puncture biopsy of deep brain lesions
The intraoperative hand-held cell microscope used in this operation is independently developed in China with a magnification of over 1000 times. It is mainly used for intraoperative diagnosis of difficult tumors, and it has high accuracy in pathological diagnosis of head and neck tumors, which is expected to become a novel technology with considerable clinical application potential, thereby promoting the development of intraoperative rapid pathological diagnosis technology.