On December 12, 2023, Professor Yuan Zuyi, President of Cardiovascular Disease Hospital of the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU), as the main research affiliation of this clinical trial, successfully completed the first patient enrollment undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) based on ultra-high resolution dual-frequency intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) imaging system. This is the world’s first-in-man (FIM) clinical study of PCI based on dual-frequency IVUS imaging system with a working frequency exceeding 100 MHz, marking a new stage of ultra-high frequency IVUS technology from scientific research to clinical application.
Ultra-high resolution dual-frequency IVUS system is jointly developed by National Innovation Center for Advanced Medical Devices (NICAMD), Shenzhen Vista Vision Medical Technology Co., Ltd. (Vista Vision, APT Medical) and Shenzhen Institute of Advanced Technology of Chinese Academy of Sciences (SIAT).
Research and development achievements of ultra-high frequency IVUS technology ascribe to major clinical requirement for precise diagnosis of early atherosclerotic plaques. This medical device consists of Cardio SpaceTM ultra-high resolution dual-frequency IVUS diagnostic system and Crystal PulsarTM disposable ultra-high resolution dual-frequency IVUS catheter. Through one single image acquisition, dual-frequency IVUS images with high resolution and large imaging depth can be obtained. Compared with traditional IVUS, the resolution of ultra-high frequency IVUS technology is almost doubled, which is expected to approach that of OCT technology. Prior to interventions, it can provide more details of the structure, abnormality and lesion of vascular walls for interventionalists, such as coronary artery dissection and calcified lesion distribution, thus supplementing more targeted information for formulating treatment regimens. After corresponding interventions, it can explicitly display the effect of stent adhesion and expansion, which provides comprehensive guidance for optimization strategies after stent implantation.
Professor Guo Ning and Attending Physician Zhang Yong completed the procedures for the first patient enrolled in this FIM study. Digital subtraction angiography (DSA) showed diffuse lesions in the proximal segment of the right coronary artery accompanied by severe stenosis, tortuous vessels and evident calcification. Intraoperatively, dual-frequency IVUS catheter was successfully delivered to the distal part of the lesion under the guidance of DSA, and imaging was performed before interventions. According to dual-frequency IVUS images of lesions and reference segments, a 3.0×33 mm stent was chosen and implanted. After sufficient dilation, dual-frequency IVUS was adopted to evaluate post-intervention effect, showing that the stent adhered to vascular wall and was properly expanded. No evident discomfort was observed during the whole operation and the patient was recovered well after operation.
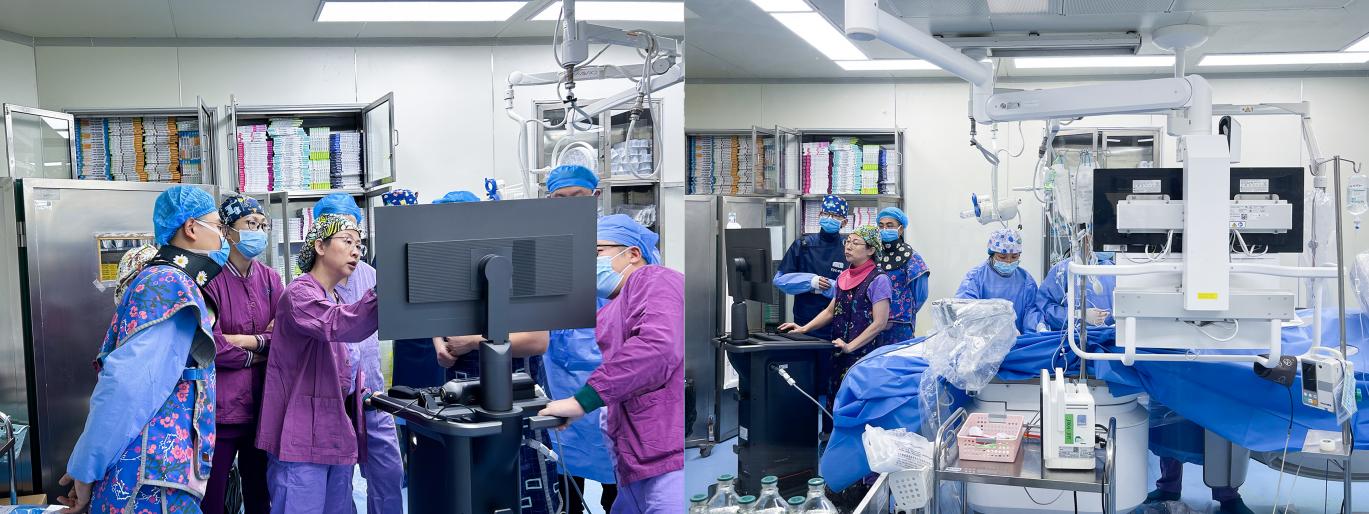
Intraoperatively, this dual-frequency IVUS possesses two advantages: high resolution and large penetration depth. It can not only display plaque load and overall structure of vessels, but also clearly show the details of dissection, calcification and stent beam, which provides more accurate guidance for formulating PCI strategy and optimizing interventional effect. Postoperatively, Professor Guo Ning stressed that the patient was diagnosed with typical diffuse lesions of the right coronary artery complicated with severe calcification. After sufficient pre-treatment, dual-frequency IVUS imaging system was employed to collect intravascular ultrasound images of patients before and after stent implantation. Full-scale structures of blood vessels can be displayed through high-depth 60 MHz images, and the details of vascular dissection can be identified via high-resolution 90 MHz images, providing more diversified intraluminal image information for evaluating interventional effect.
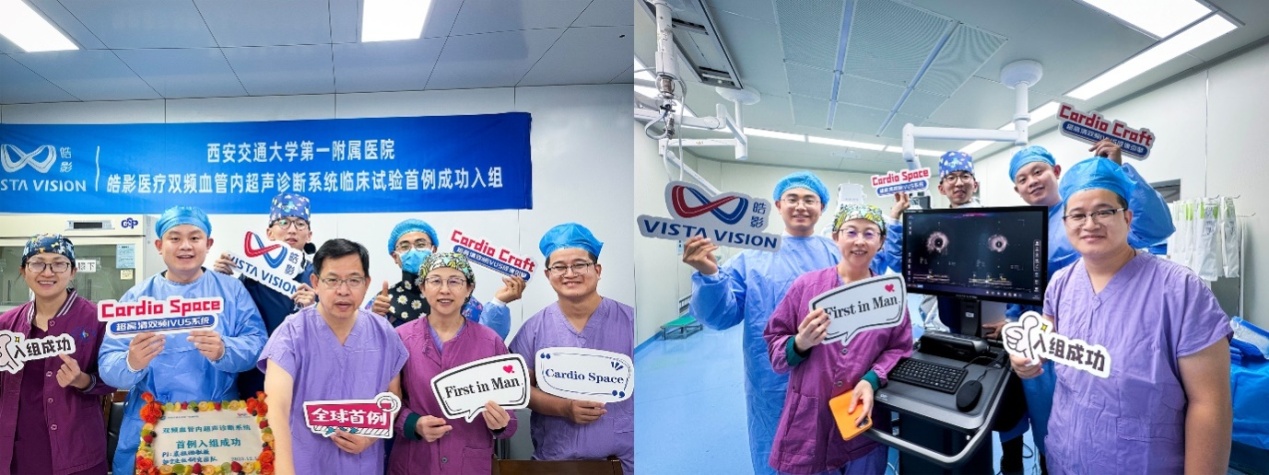

Yuan Zuyi highlighted that ultra-high resolution dual-frequency IVUS, as an innovative technology, has achieved a breakthrough in the working frequency of IVUS, and has complementary advantages of simultaneously obtaining images with large depth and high resolution. We look forward to exploring application potential of this intraluminal imaging technology in guiding PCI in more extensive clinical trials.
Liu Xin, CEO of NICAMD, believes that success of this procedure using innovative medical devices marks a major breakthrough in innovative technologies in the field of cardiology in China, which is expected to provide a more rapid, accurate and effective technical approach for the diagnosis and treatment of coronary artery diseases.