On February 22, 2022, the team led by Professor Liu Bing and Professor Wang Yawen from the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi 'an Jiaotong University (XJTU) published an online article entitled" Bacteriophage protein GP46 is a new cross-species inhibitor of nuclear-associated HU proteins" in PNAS, illustrating significant research results in the field of bacteriophage bacteriostasis, antibacterial and antimalarial strategies. In this article, molecular mechanism of broad-range antibacterial and antimalarial capabilities and new targets of Gp46 protein were unraveled, which exerts profound influence on phage, histone, research and development of antibiotics and antimalarial agents, etc.

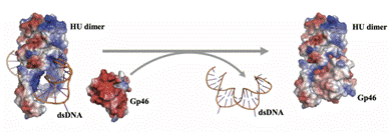
The team led by Liu Bing and Wang Yawen employed nuclear magnetic resonance technology to elaborate the exact mechanism of bacteriophage protein Gp46 inhibiting bacteria by binding to bacterial histone, becoming the first worldwide to identify the antibacterial gene of phage-encoded bacterial histone-like HU protein. The expression of Gp46 can elongate the cell body of bacterial strain, make the nucleus-like region disappear, and finally lead to bacterial death. Histone-like proteins are highly conserved among bacteria and Apicomplexanparasites. Consequently, Gp46 is a new category of broad-spectrum antibacterial protein. In this study, Gp46 can inhibita wide range of bacteria including Staphylococcus aureus, Acinetobacterbaumannii, Klebsiellapneumoniae and clinically significant drug-resistant bacteria, as well asApicomplexan parasites (including Plasmodium falciparum and Toxoplasma gondii), laying a solid foundation for the prevention and treatment of drug-resistant bacteria and Plasmodium falciparum.
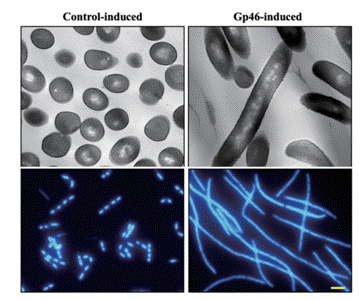
Upper panel: Gp46elongatesthecell body ofbacteria,prevents celldivision andcauses cell death
Lower panel: The molecular mechanism of Gp46inhibiting bacteria by blockinghistone from binding to bacterial DNA
This study is another groundbreaking achievement after the team published an article in Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.97) in October 2021, which discovered a novel antibacterial mechanism. This original article was solely completed by XJTU. All the first and corresponding authors are from XJTU. Zhang Peipei, a postdoctoral fellow from Liu Bing’s team, Zhao Xiaohui, a doctoral student from XJTU Health Science Center, and Professor Wang Yawen from Department of Laboratory Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital of XJTU are the first authors. Professor Wang Hongliang and Professor Liu Bing are the corresponding authors. Department of Laboratory Medicine of our hospital is the first and corresponding affiliation. The design, implementation and drafting of this work were all carried out in our hospital, which played a critical role in the research of pathogenic microorganisms and the construction of related disciplines of our hospital.

This study is one of the key projects supported by the construction of national medical center, and financially supported by Key Project of Ministry of Science and Technology of China, National Natural Science Foundation of China and Key Research and Development Plan of Shaanxi Province. Instrument Analysis Center of XJTU provided experimental assistance for nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Article link: https://www.pnas.org/content/119/9/e2116278119.short?rss=1