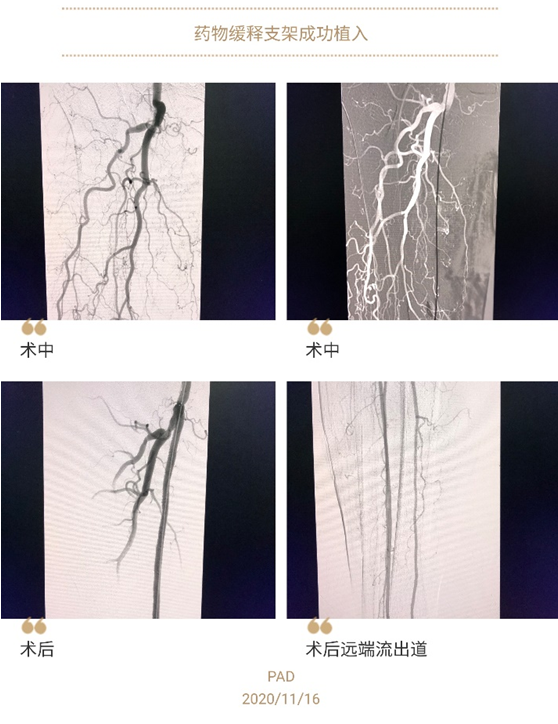
On November 16, 2020, under the leadership of Director Liu Jianlin, surgeons from Department of Vascular Surgery of the First Affiliated Hospital of Xi’an Jiaotong University (XJTU) successfully implanted a sustained-release drug-coated stent for an 80-year-old patient with superficial femoral artery occlusion of the right lower extremity. The length of occluded blood vessel of this patient was up to 30cm. After stent implantation, the blood flow of the occluded superficial femoral artery of the right lower extremity was immediately recovered and the postoperative ABI (Ankle Brachial Index) on the right side was increased from 0.31 to 0.86, indicating that the ischemic symptoms of this patient were completely improved. This stent is the world's first polymer-coated sustained-release stent for peripheral artery, which fills the gap in the field of PAD treatment in China, possesses a revolutionary technology for 365-d sustained-release and completely covers the process of restenosis.
In China, the incidence rate of arteriosclerosis obliterans of the lower limbs is approximately 10%. Over aging, the incidence rate is on the rise. The incidence rate in population aged>70 years old ranges from 15% to 20%. Clinical manifestations include cold, numbness, weakness and intermittent claudication of the lower limbs. In severe cases, it can cause ischemic resting pain, ulcer, gangrene of the lower limbs and other symptoms, which severely affect the quality of life of these patients and cause a heavy burden to both family and society.
Endovascular treatment of arterial diseases of the lower extremity has underwent a evolutionary history from "simple balloon dilation", "pre-balloon dilation+metal stent implantation" and then to "drug-coated balloon dilation". Restenosis or even occlusion after bare metal stent implantation is the main reason that impedes the treatment. Drug-coated balloon can inhibit plaque enlargement and intimal hyperplasia after balloon dilation, whereas it is not suitable for highly elastic retraction lesions. Sustained-release drug-coated stent can properly suppress intimal hyperplasia surrounding the distal end of stent after stent implantation, and then prevent the incidence of restenosis within the stent. Besides, it can resolve the problem of insufficient support for the lumen after drug-coated balloon dilation. Consequently, it has been reported that the 1-year patency rate of low-dose paclitaxel sustained-release stent achieves 92.1% and 82% for the 2-year patency rate, which yields favorable postoperative clinical efficacy. Favorable clinical efficacy during 3-year follow-up has been reported abroad. On July 17, 2020, the stent was approved for clinical use via the Green Channel by National Medical Products Administration in China. As one of the first-batch of centers with the permit to apply this stent in China, Department of Vascular Surgery of our hospital has successfully completed the first case of sustained-release drug-coated stent implantation in Northwest China.