In recent years, immunotherapy, represented by immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), has revolutionized the treatment of various advanced tumors, significantly improving patient survival rates. However, acquired resistance and immune-related adverse events (irAEs) are two critical challenges limiting the effectiveness of ICIs.
To investigate the potential mechanisms behind acquired resistance to ICIs, the research team analyzed melanoma immunotherapy samples. They discovered that chaperone-mediated autophagy (CMA) activity in melanoma is significantly higher than in other tumor types. They further found that positive relationship between CMA and PD-L1 expression level was induced by IFN-γ mediated compensatory upregulation of PD-L1 and CMA, accompanied by enhanced macropinocytosis. Building on this discovery, the team designed prion-like microprotein drugs (SAP) based on chiral peptides (PHA) through GSH-regulated reversible self-assembly. These drugs can rewire CMA to recognize PD-L1 and induce its degradation via the lysosomal pathway.
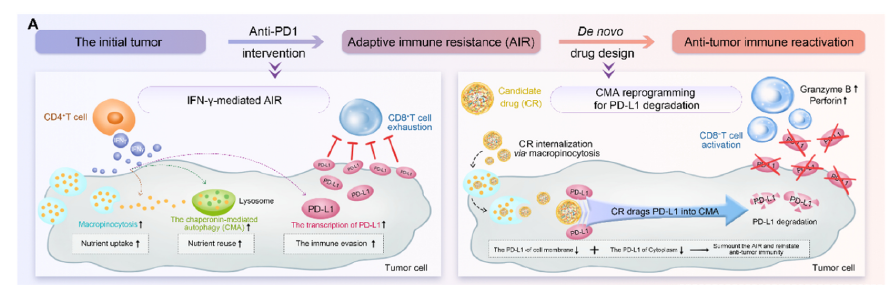
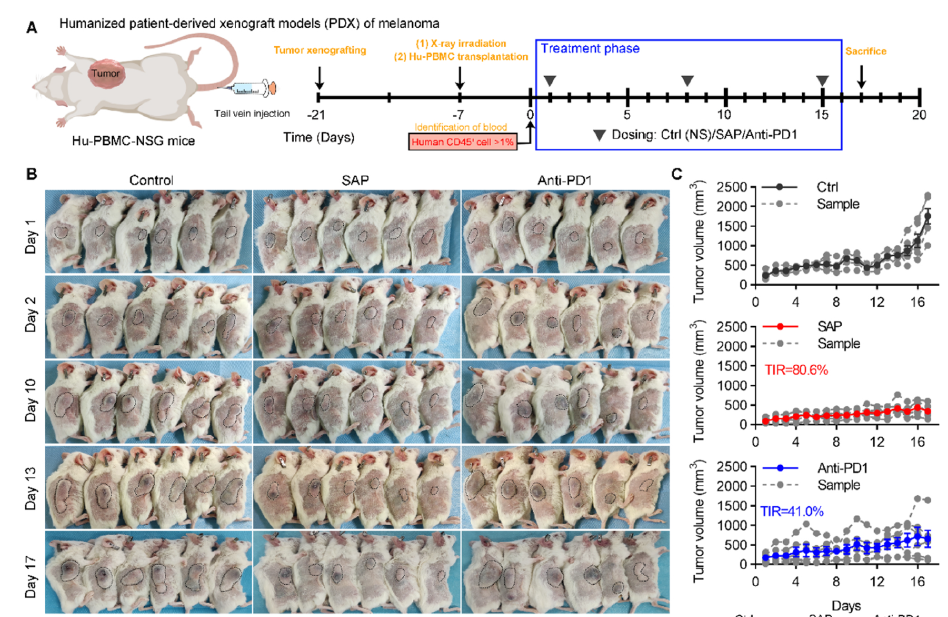
This work, titled "Rewiring Chaperone-Mediated Autophagy in Cancer by a Prion-like Chemical Inducer of Proximity to Counteract Adaptive Immune Resistance," was published in the prestigious journal Drug Resistance Updates (Impact Factor 24.3). The study's corresponding author is Prof. He Wangxiao from the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU), with Prof. Yan Jin and Dr. Liu Dan as co-first authors. The article became an ESI Hot Paper immediately upon its online.
To avoid the occurrence of immune-related adverse events (irAEs), particularly checkpoint inhibitor-related pneumonitis (CIP) in lung cancer immunotherapy, and to break through the "forbidden zone" of treating lung cancer with ICIs in patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), the research team developed a novel erythrocyte membrane (RBC) biomimetic supramolecular ICI protein (EMS-PDBP) based on biomimetic nanomedicine strategies. EMS-PDBP enables precise immunotherapy for IPF-associated lung adenocarcinoma by selectively targeting PD-L1 degradation in tumor cells through unique endocytic mechanisms of tumor cells, macrophages, and lung fibroblasts.
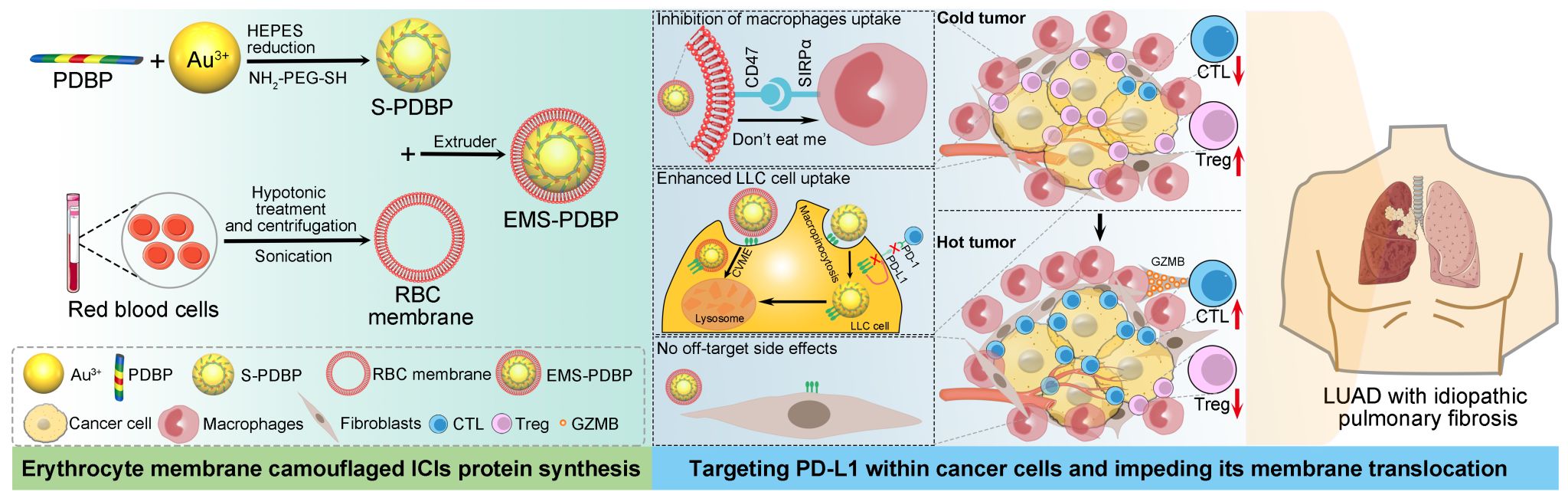
This study, titled "Advancing the Boundaries of Immunotherapy in Lung Adenocarcinoma with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis by a Biomimetic Proteinoid Enabling Selective Endocytosis," was published in the journal ACS Nano (Impact Factor 17.1). The corresponding author is Prof. He Wangxiao, with Ph.D. student Jiang Aimin as the first author.