The dosage of general anesthesia drugs is large, which constantly causes multiple adverse reactions. In the research of general anesthetic drugs for anesthetic efficacy enhancement and toxicity reduction, use of nano-carrier precise drug delivery technology and combining two different anesthetic drugs to achieve anesthetic efficacy enhancement and toxicity reduction has attracted widespread attention at home and abroad. However, nano-carriers of anesthetic drugs have been rarely reported, and nano-carrier compounds loaded with two different anesthetic drugs have not been reported. On one hand, the fundamental reason is that most general anesthetic drugs are fat-soluble small molecules, and few suitable nano-carriers can simultaneously load general anesthetic drugs with different properties. On the other hand, because general anesthetic drugs play an anesthetic role by passing through the blood-brain barrier (BBB), it is difficult for the existing nano-carrier technology to pass through the BBB rapidly and effectively.
To resolve these challenges, Gao Wei, Deputy Chief Physician from Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine of the First Affiliated Hospital (FAH) of Xi'an Jiaotong University (XJTU), cooperated with Professor Wu Daocheng, Visiting Professor from School of Life Science and Technology of XJTU, and proposed to utilize special bridging molecule monoglyceride monooleate (GMO) to form Trimolecular aggregates of propofol and etomidate, and then used the surfactant F127 as a template to form four-in-one molecular aggregates in the water phase, and finally brain-targeted lactoferrin was connected to the surface of the aggregates to form LF-four-in-one molecular aggregates. The particle size of the four-in-one aggregates is (106.7±8.1) nm, and the lactoferrin on the surface is approximately 10 nm. It can efficiently load different general anesthesia drugs of propofol and etomidate simultaneously, and rapidly release two anesthetic drugs to reach GABA receptors simultaneously in the lipophilic environment of the brain, thus realizing the synergistic inhibition of propofol and etomidate on GABA receptors and achieving remarkable anesthetic efficacy enhancement and toxicity reduction (Figure 1). In addition, the enrichment of brain-targeted molecule lactoferrin and the new method of ultrasound combined with microbubbles opened the BBB, a remarkable 4.5-fold enhancement in brain drug delivery was achieved. The dosage of anesthetic drugs was significantly reduced, and the synergistic anesthesia of two general anesthetic drugs on GABA receptor was achieved.
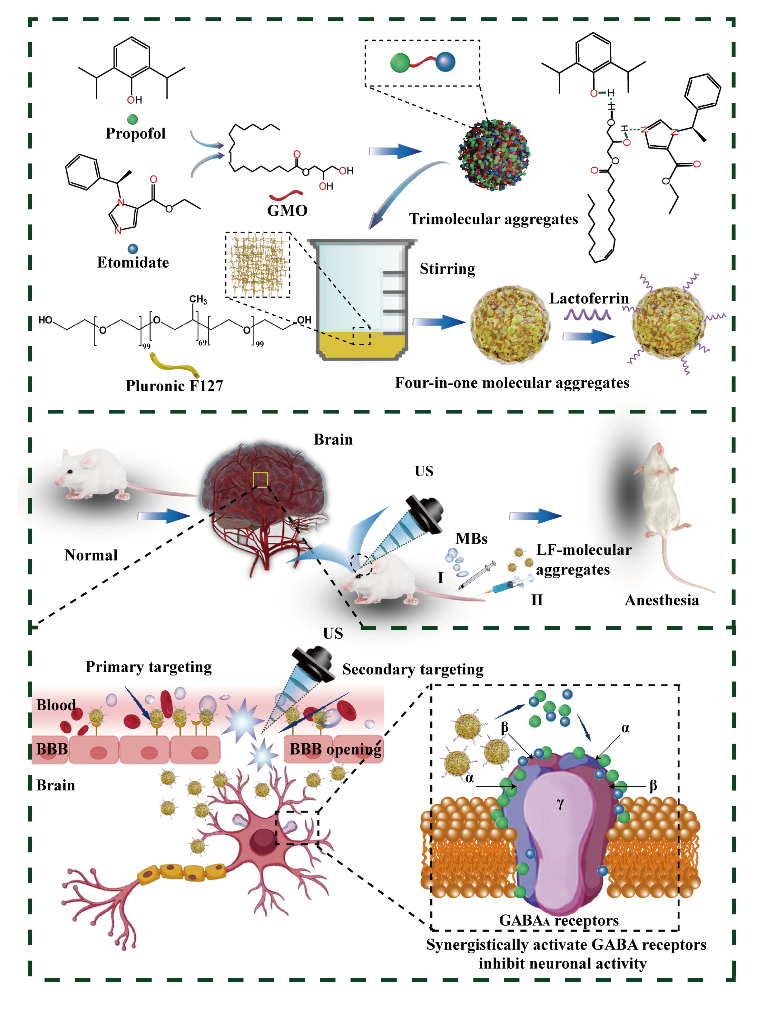
Figure 1. Design and preparation of LF modified four-in-one molecular aggregates and ultrasound-assisted synergistic anesthesia
Experiments show that the interaction index of two general anesthesia drugs is 0.289, suggesting a significant improvement in synergistic anesthesia effectiveness. The effective dose (ED50) is significantly reduced (from 5.6 mg kg-1 to 2.52mg kg-1), and the therapeutic index (7.905) is significantly higher than that of two drugs combined (3.839) currently used in clinical practice. The changes of heart rate parameters and blood pressure in the molecular aggregate group are relatively slow, quite similar to the data in the normal group. Electroencephalogram (EEG) experiments demonstrate a significant elevation in the proportion of δ waves from 28% to 80% for aggregates, accompanied by a nearly fivefold reduction in the proportion of θ waves, meaning a significant improvement in synergistic anesthesia effectiveness with lower drug dosage. These results indicated that the depth of anesthesia was increased significantly. These data collectively demonstrate that LF-molecular aggregates can significantly enhance anesthetic efficacy and reduce toxicity with ultrasound assistance. The anesthesia mechanism was explored and validated by C-Fos protein. This study integrates the molecular simulation, BBB opening by ultrasound, molecular aggregates, physiology and EEG, achieving significant achievements in engineering medicine.
Relevant research results were published as an article entitled "Ultrasound Combined Blood-Brain Barrier Targeting Brain Delivery of Four-in-one Molecular Aggregates for the Enhancement of Anesthetic Efficacy and Toxicity Reduction via Propofol-etomidate Synergistically Inhibition GABA Receptor" in Aggregate (IF=18.8). PhD student Zhang Shuo from School of Life Science and Technology of XJTU is the first author. Professor Wu Daocheng from School of Life Science and Technology of XJTU, and Deputy Chief Physician Gao Wei, Deputy Director of Department of Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine of FAH, are co-corresponding authors of this article.
Article link: https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.573